Dual boot for Windows and Linux enhances the realm of computing by offering the flexibility of running two operating systems on a single machine as a powerful feature. In the realm of computing, the flexibility of running two operating systems on a single machine is a powerful feature. This is where dual-booting comes into play, allowing users to enjoy the best of both worlds.
The widespread compatibility and user-friendly interface of Windows alongside the robustness and open-source nature of Linux. Setting up a dual-boot system can seem daunting at first, but by following a structured approach, you can efficiently configure your computer to run both Windows and Linux. This article will lead you through the procedure, one step at a time.
Step 1: Backup Your Data
The first and most crucial step is to back up your important data. Alterations to your system’s partitions and the installation of a new operating system carry a risk of data loss. Use an external hard drive or cloud storage to secure your files, ensuring you can recover them if anything goes awry.
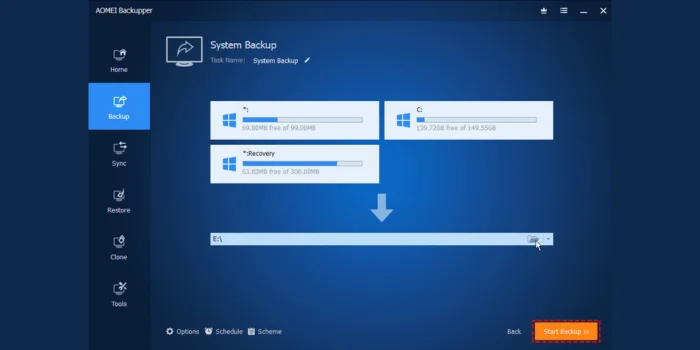
Step 2: Prepare Your System
Before proceeding with the dual-boot setup, there are a few preparatory actions to take:
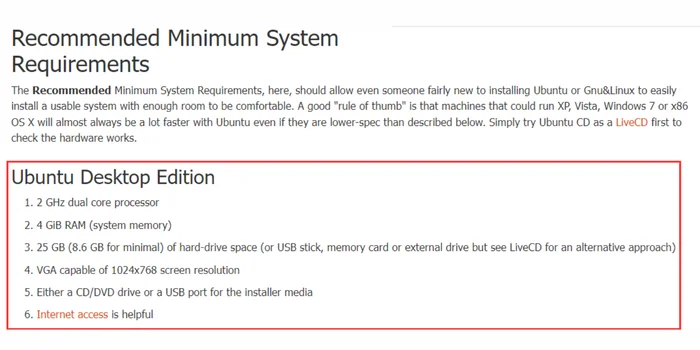
- Check System Requirements: Verify that your computer meets the minimum hardware requirements for the Linux distribution you intend to install.
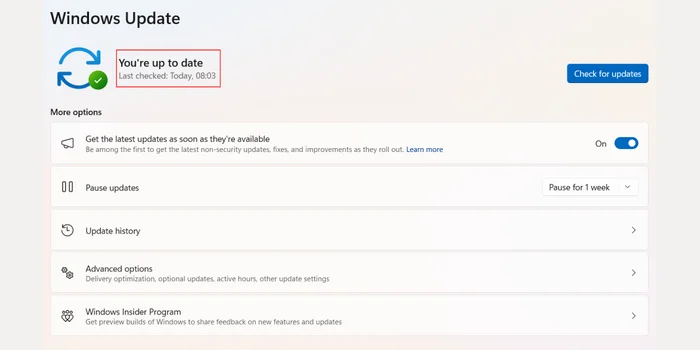
- Update Windows: Ensure your Windows installation is up to date to prevent any compatibility issues.
- Disable Fast Startup and Secure Boot: These features can interfere with the installation process. Fast Startup can be turned off through the Control Panel, while Secure Boot is disabled in the BIOS/UEFI settings.
Step 3: Partition Your Hard Drive
Next, you’ll need to create space on your hard drive for Linux:
- Shrink the Windows Partition: Using the Windows Disk Management tool, reduce the size of your Windows partition to free up space.
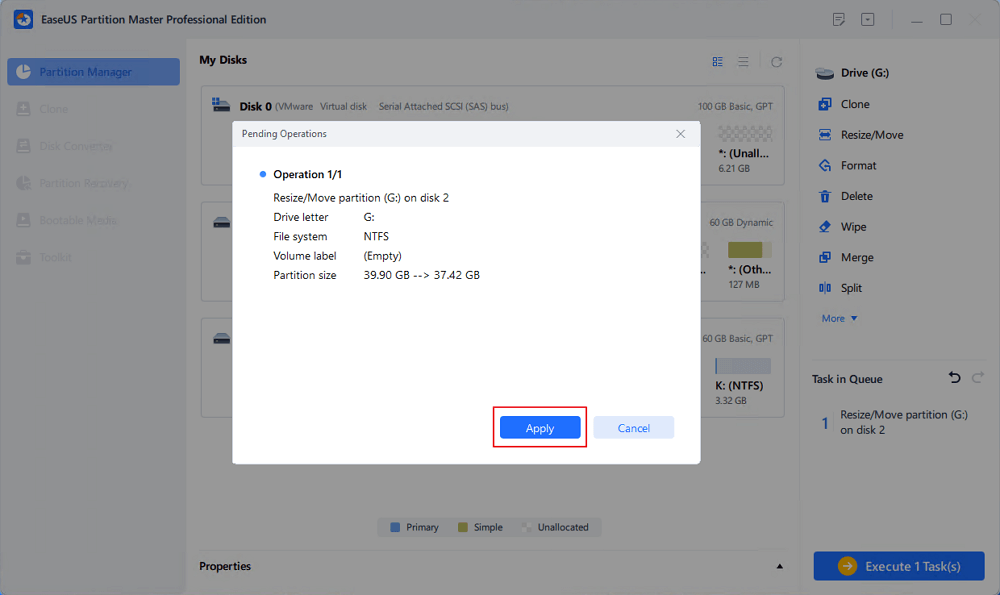
- Create Free Space for Linux: Leave the newly created space unallocated. The Linux installer will recognize this space and install Linux there.
Step 4: Create a Linux Installation Media
- Download the Linux ISO: Choose a Linux distribution and download its ISO file.
- Create a Bootable USB Drive: Use software like Rufus or Etcher to make a USB drive bootable with the Linux ISO.
Step 5: Boot from the Installation Media
- Change the Boot Order: Access your computer’s BIOS/UEFI settings and change the boot order to prioritize the USB drive.
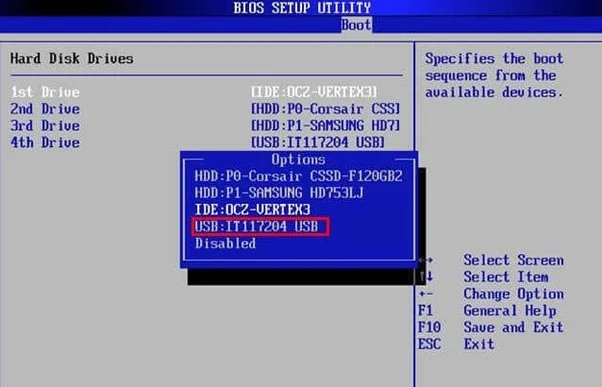
- Boot into Linux Installer: If successful, your computer will boot from the USB into the Linux installation environment.
Step 6: Install Linux
During the installation process:
- Choose Installation Type: Opt to install Linux alongside Windows Boot Manager. This is crucial for setting up a dual boot.
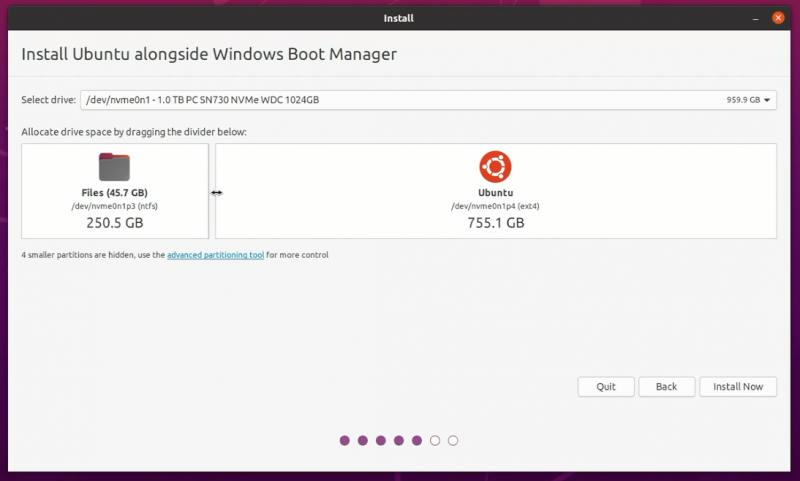
- Partitioning: Advanced users can manually partition their drives. Most users should let the installer handle this step.
- Follow On-Screen Instructions: Complete the installation by following the prompts, including setting up your user account.
Step 7: Setup Dual Boot
The installation process should install GRUB (GNU GRand Unified Bootloader), allowing you to choose between Windows and Linux at startup. After installation, restart your computer. You should see a GRUB menu that lets you select the operating system you wish to boot into.

Step 8: Finalize Installation
Upon your initial startup into Linux:
- Update Linux: Check for updates and install them to ensure your system is secure and up to date.
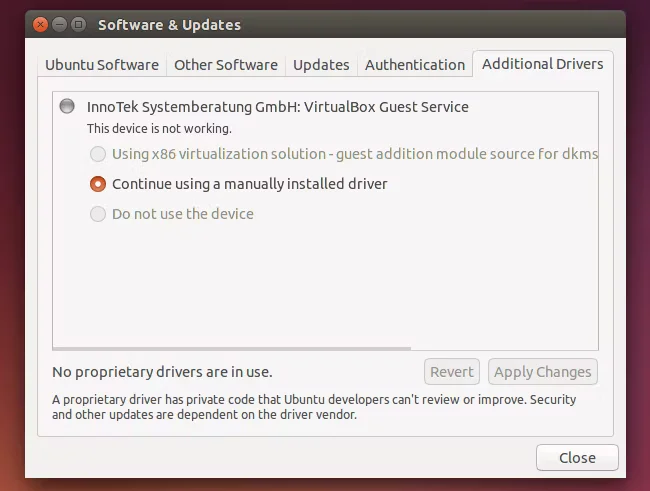
- Install Drivers and Software: Install the necessary drivers for your hardware and any software you need.
Step 9: Troubleshooting
Should you encounter issues:
- Boot Issues: Use a live USB drive to repair the bootloader if you cannot boot into one of the operating systems.
- Driver Issues: You may need to install proprietary drivers for certain hardware components.
Also Read This: Installing Windows on your Chromebook: A Step-by-Step Guide.
Enjoy Your Dual-Boot System
Congratulations! You’ve successfully set up a dual-boot system with Windows and Linux. This setup offers you the flexibility to choose between operating systems based on your needs, providing a powerful tool for a wide range of computing tasks.
While this article provides a general framework for setting up a dual-boot system, remember that specific steps may vary depending on your hardware and the Linux distribution you choose. Always consult the official documentation of your chosen distribution for detailed guidance and support.
Enjoy the journey into dual-booting, a gateway to a more versatile and capable computing experience.



