Introduction
In the fast-paced and interconnected world of today, communication is the backbone of progress. At the heart of this connectivity lies the Wide Area Network (WAN), a technology that has revolutionized the way we share information and collaborate on a global scale.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of WAN, understanding their significance, evolution, and the impact they have on shaping our modern digital landscape.
Understanding WAN
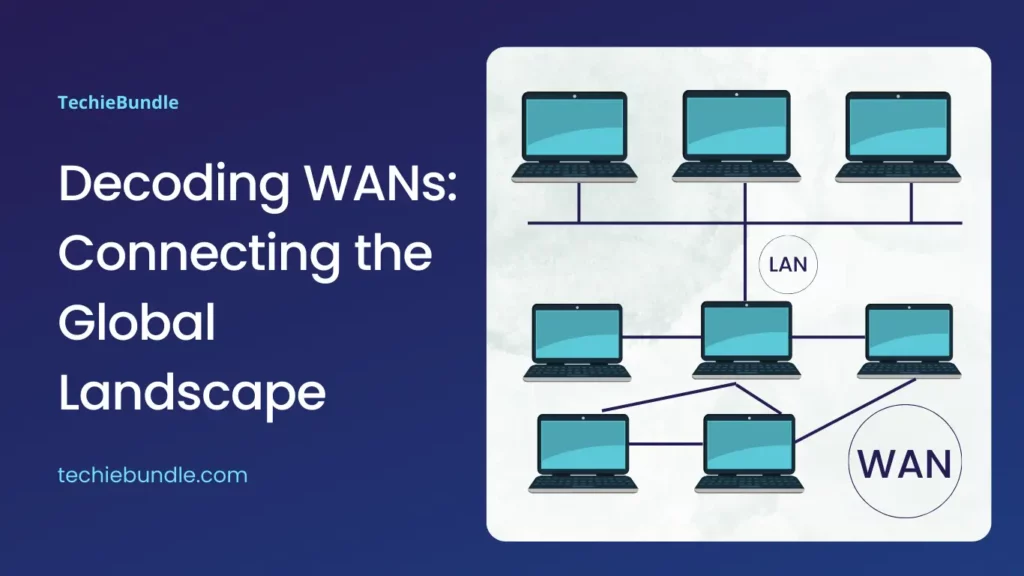
A Wide Area Network, or WAN, is a network that spans a large geographic area, connecting multiple Local Area Networks (LANs) or Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs). Unlike LANs, which are confined to a single location like an office or a campus, WAN extend across cities, countries, or even continents. This expansive reach enables organizations to establish seamless communication channels between distant locations.
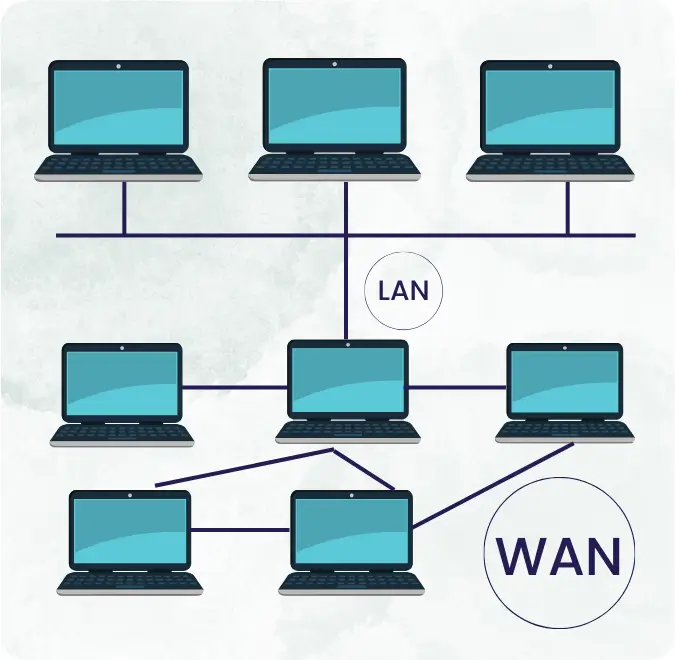
WAN facilitate the transfer of data, voice, and video across vast distances, making them essential for businesses, governments, and individuals alike. The internet itself can be considered a global WAN, connecting people, businesses, and institutions around the world.
Evolution of WAN
The concept of wide area networking has evolved significantly since its inception. In the early days, WAN relied on dedicated communication lines, such as point-to-point leased lines, to establish connections between remote locations. This method was not only expensive but also limited in terms of scalability.
The advent of packet-switching technology, most notably the development of the Internet Protocol (IP), transformed the landscape of wide area networking. The ability to break down data into packets and transmit them independently over a shared network infrastructure revolutionized data communication. This paved the way for the creation of the internet as we know it today.
Key Components of WAN
- Routers: Router play a crucial role in WAN by directing data packets between different networks. They analyze destination addresses and determine the most efficient path for data transmission.
- Switches: Switches are responsible for creating a network by connecting multiple devices within the same LAN. In the context of WAN, switches are often used in combination with routers to manage data traffic.
- Transmission Media: WAN use various transmission media, including fiber-optic cables, satellite links, and microwave connections, to transmit data over long distances.
- Protocols: Standardized protocols ensure interoperability between different devices and networks. Common WAN protocols include TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol), MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching), and Frame Relay.
- Security Measures: Given the expansive nature of WAN, security is a paramount concern. Encryption, firewalls, and virtual private networks (VPNs) are employed to protect data during transmission.
Benefits of WAN
- Global Connectivity: WAN break down geographical barriers, allowing seamless communication and collaboration between individuals and organizations located in different parts of the world.
- Resource Sharing: WAN enable the sharing of resources such as files, applications, and databases across distributed locations. This promotes efficiency and productivity within organizations.
- Cost Efficiency: While the initial setup of WAN infrastructure may require significant investment, the long-term cost benefits are substantial. Organizations can centralize IT resources and reduce the need for duplicate infrastructure at each location.
- Scalability: WAN are designed to scale, allowing organizations to expand their network infrastructure as needed. This scalability is vital for accommodating the growth of businesses and adapting to changing requirements.
Challenges and Considerations
- Latency: The transmission of data over long distances introduces latency, which can impact real-time applications. Technologies like Quality of Service (QoS) are employed to prioritize certain types of traffic and minimize latency.
- Security Concerns: The expansive nature of WAN makes them susceptible to security threats. Organizations must implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data during transmission.
- Maintenance and Management: Managing a WAN requires specialized skills, and organizations must invest in the training of IT personnel. Regular maintenance and updates are essential to ensure optimal performance.
- Bandwidth Limitations: While technology has advanced, bandwidth limitations can still be a challenge in certain regions. This can affect the speed and efficiency of data transmission.
[ You might also like: APIs Unveiled: Understanding the Basics with Examples ]
Conclusion
Wide Area Networks have become an integral part of our connected world, shaping the way we communicate, collaborate, and conduct business on a global scale. From the early days of dedicated communication lines to the modern, interconnected internet era, WAN have evolved to meet the ever-growing demands of our digital society.
As technology continues to advance, the role of WAN will undoubtedly expand, contributing to the continued transformation of our interconnected world.